

Medically Reviewed by Zilpah Sheikh, MD on January 14, 2024
Written by WebMD Editorial ContributorsDepo-Provera is a birth control method that you can get as a shot. You might hear people call it a contraceptive injection or birth control shot. It’s a man-made hormone, medroxyprogesterone, which is similar to the natural hormone progesterone.
You get the shot in your arm or buttock. If you get your shot at the doctor's office, your clinician will inject Depo-Provera deep into your muscle or under your skin. You have to get it every 12 weeks to get full protection.
After your first injection, doctors recommend that you use a backup birth control method (like a condom) for 7 days.
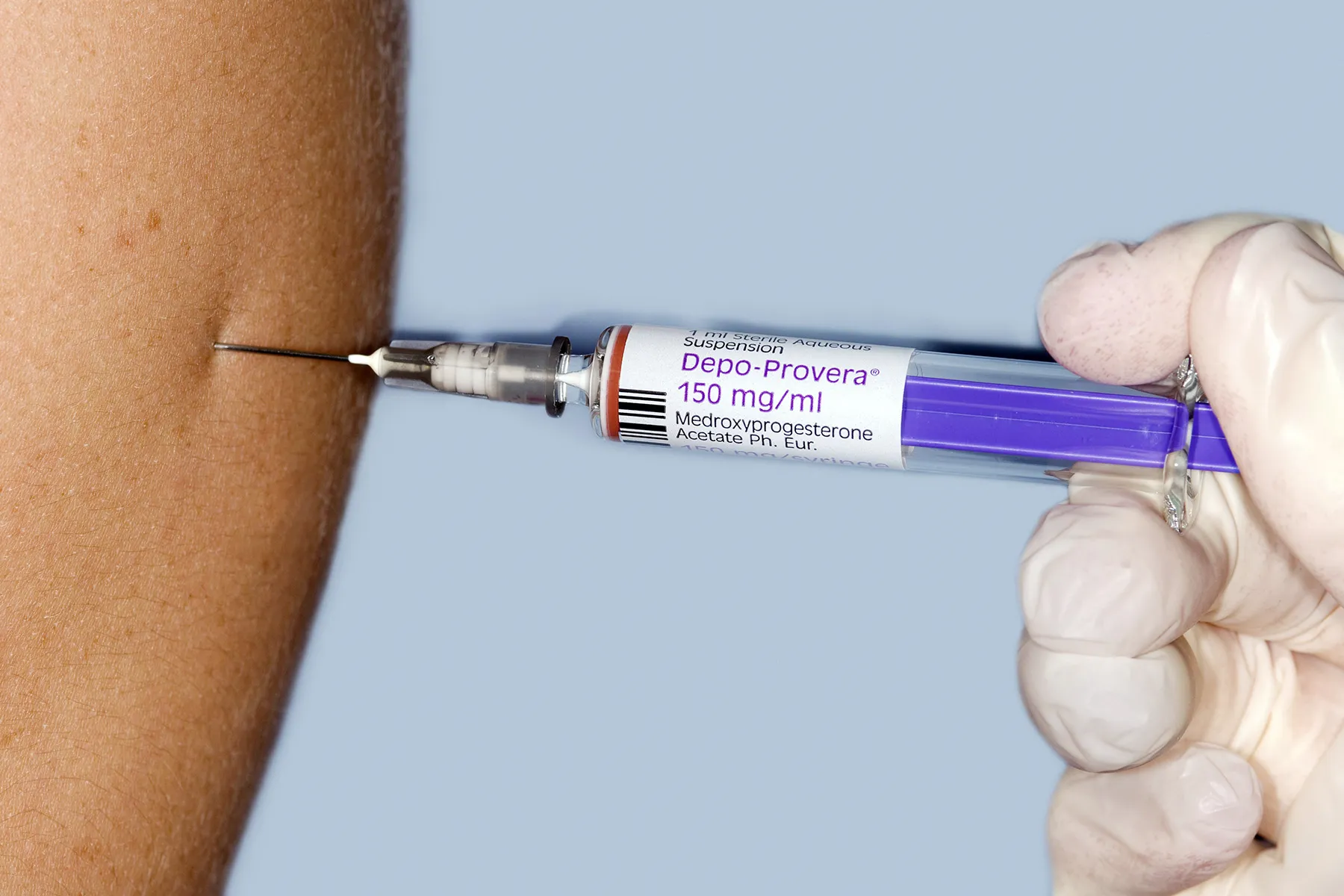
You can also get a version of Depo-Provera that you inject at home. This version of the shot is only subcutaneous, which means it goes into your skin instead of deep into your muscle.
Experts call the at-home shot Depo-subQ Provera 104. It's a prefilled, single-use syringe with a smaller needle than the one your doctor uses, so it may hurt less. It also uses a lower dose of progestin than the 400 milligrams in the dose from your doctor. You'll need to give yourself a shot in the thigh or belly every 12 weeks in order for it to work.
Your doctor can show you (in person or through telemedicine) how to inject yourself and safely throw away sharp tools after your shot. It's important to follow their guidance. At-home Depo-Provera is safe to use. It's not likely, but if you notice a reaction at the injection site, let your doctor know.
You may notice a lump, dimple, or dent at the reaction site. You may also see redness, bruising, blistering, or itchiness.
If you think something is not right, call your doctor right away. They can help clear up confusion or guide you while you use Depo-Provera at home.
Both the original and at-home versions are 99% effective at preventing pregnancy if you get it every 3 months, as directed. But because that isn't always possible, typical effectiveness is around 94%. That means for every 100 women who get the shot, about 6 will get pregnant.
Here's how that stacks up against other types of reversible (nonpermanent) birth control:
How long does the Depo-Provera shot take to work?
Depo-Provera starts to work as birth control right away if you get it within the first 5 days of your period. You may have to wait 7 to 10 days before having sex without a condom if you get the shot at another time during your cycle.
What happens if I'm late getting my Depo-Provera shot?
You're more likely to get pregnant if you're more than 2 weeks behind schedule in getting your shot. Use another form of birth control to be safe.
The hormone works on your pituitary gland, causing your ovaries to stop sending out eggs. Without eggs, you can't get pregnant. It also changes the lining of your uterus and the mucus in your cervix. That makes it harder for sperm to reach any eggs that might be released.
The side effects for the birth control shot are the same for both the original version and the at-home one. You might notice:
Changes to your menstrual cycle are the most common side effects. After a year of use, about 50% of women will stop getting their periods. If this happens to you, your period should come back when you stop getting the shots.
Talk to your doctor immediately if you have trouble breathing, pain, itching, or bleeding at the site of the shot, severe stomach pain, an allergic reaction, depression, heavy bleeding, or other symptoms you're unsure about.
Depo-Provera long-term side effects
Long-term use of Depo-Provera may cause you to lose bone mineral density, which makes you more likely to get osteoporosis. Your chances are higher if you've taken the shot for longer than 2 years, especially if osteoporosis runs in your family, if you drink a lot, if you smoke, or if you have other risk factors for the condition.
A few women have reported flu-like symptoms and unusual bleeding after stopping Depo-Provera, but there isn't much research on whether these things are linked. Other women report symptoms similar to the known side effects.
It's OK for most people. But you shouldn't get it if you have:
Your doctor will be cautious about giving it to you if you're a teenager or if you have:
Depo-Provera age limit
The exact age when a woman is still able to get pregnant is unknown. It's recommended that women who do not want to become pregnant keep using birth control until menopause or around age 50 to 55 years. If you're of advanced reproductive age, your doctor can recommend the proper form of birth control, as there can be some risks with continuing birth control until menopause, including blood-clotting, stroke, and breast cancer.
Depo-Provera weight limit
Unlike the patch and pill forms of birth control, which studies show to have decreased effectiveness in women with obesity, the birth control shot is considered to be safe and effective in women with obesity. Also, changes to the dosage amount don't have to be made based on body weight.
If you have obesity, it's important to talk to your doctor about the best birth control method for you. Weight gain is a side effect of Depo-Provera. Also, women with obesity are at higher risk of side effects of birth control, including thrombotic events like blood clots.
You can become pregnant as soon as 3 to 4 months after your last shot. But it takes some people several months to conceive after they stop using this type of birth control. The time frame doesn't seem to be linked to how long you got the shots.
In addition to preventing pregnancy, the benefits of Depo-Provera include:
Injections may be free or cost up to $150 each, depending on your insurance. They may be cheaper at family planning clinics.
DOCTOR DISCUSSION GUIDE
Planning to Talk to Your Doctor About Birth Control?